|
|
The Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AIRSAR) is an
all-weather imaging tool able to penetrate through clouds and collect data at night.
The longer wavelengths can also penetrate into the forest canopy and in
extremely dry areas, through thin sand cover and dry snow pack. AIRSAR was
designed and built by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) which also manages
the AIRSAR project.† JPL, a division of
the California Institute of Technology, is a lead research and development
center for the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). AIRSAR
serves as a NASA radar technology testbed for demonstrating new radar
technology and acquiring data for the development of radar processing techniques and applications.
As part of NASAís Earth Science Enterprise, AIRSAR first
flew in 1988 and continues to conduct at least one flight campaign each year,
either in the United States or on an international mission.†
A
Flying Laboratory AIRSAR
instrument (panels behind wing) mounted aboard a modified NASA DC-8
aircraft. During data
collection, the plane flies at 8 kilometers over the average terrain
height at a velocity of 215 meters per second.
|
|
|
AIRSAR is a side-looking radar instrument and can collect
fully polarimetric data (POLSAR) at three radar wavelengths: C-band (0.057 m), L-band
(0.25 m), and P-band (0.68 m).†
AIRSAR
can also collect two types of interferometric data: cross-track interferometric
data (TOPSAR), which are sensitive to topography and along-track
interferometric (ATI) data, which can be used to measure ocean surface
currents.†
(TOPSAR), which are sensitive to topography and along-track
interferometric (ATI) data, which can be used to measure ocean surface
currents.†
AIRSAR Instrument-Antennas
The
AIRSAR radar antennas on the back part of the DC-8 aircraft. These antennas are used to collect data in all three modes.
L-band ATI uses an additional antenna (not shown) located in front
of the wings.
|
|
|
AIRSAR provides three operational modes:
POLSAR: P-, L-, C-band full polarization
TOPSAR
XTI1:† C-band VV, C-band DEM, P- and L-band full
polarization
††††
XTI2:† C- and L-band VV and DEMs, P-band full
polarization
ATI†††††††††
C-band
and L-band;† VV polarization only
In POLSAR mode, fully polarimetric data are acquired at
all three frequencies.† Fully
polarimetric means that radar waves are alternatively transmitted in
horizontal (H) and vertical (V) polarization, while every pulse is received in
both H and V polarizations.† 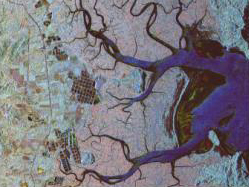 POLSAR data are sensitive to the geometry (including vegetation) and dielectric properties (water content) of the terrain.
POLSAR data are sensitive to the geometry (including vegetation) and dielectric properties (water content) of the terrain.
Land
Classification
Polarimetric
data over coastal Thailand in an area of mangrove forests along the coast,
agriculture and fish farming (square ponds).
|
|
|
In
TOPSAR mode, AIRSAR collects interferometric data using C- and L-band
vertically-displaced antenna pairs to produce digital elevation models (DEM's).
The radars which are not being used for interferometry (P-band for XTI2 or
P-band and L-band for XTI1) collect quad-pol data co-registered with the
C-band DEM. Interferometric data can be collected in
"ping-pong" mode, where each antenna is used alternately for
transmit and the effective baseline is doubled, and in
"common-transmitter" mode where only one antenna is used for
transmit.
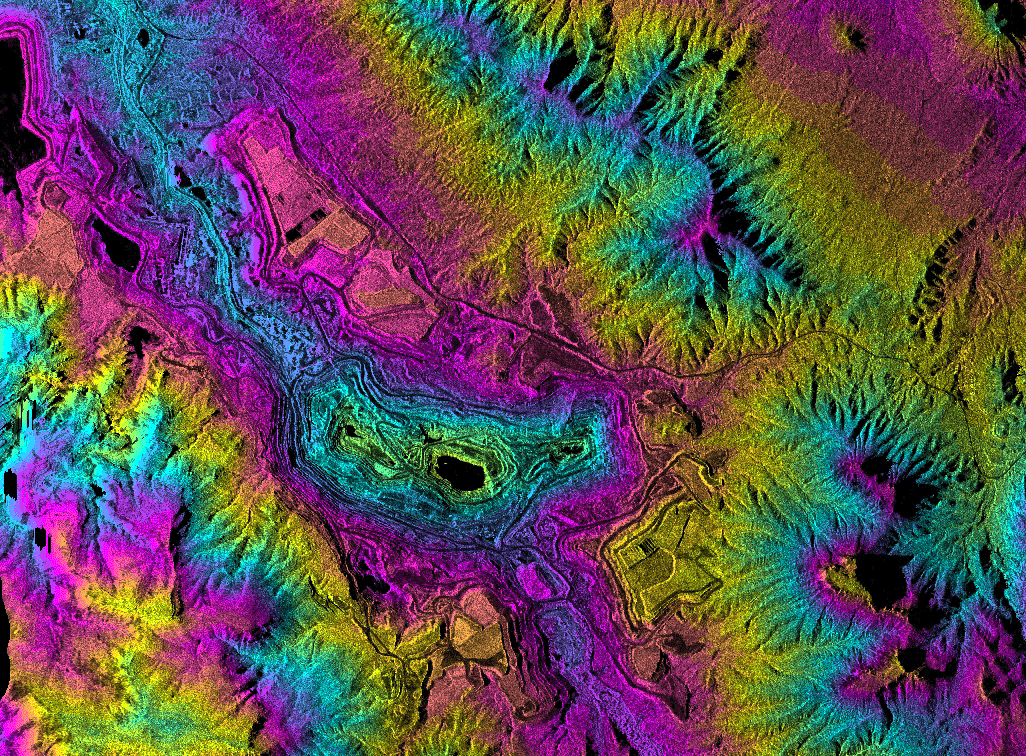
Topographic
Mapping Topographic
radar data over the Ray Mine in central Arizona. Colors show elevation information from the mine pits in the
center of the image up through the surrounding mountains.
These data are being used for mine site and
watershed
characterization associated with
environmental assessment of the area.
|
|
|
ATI Data (Experimental)
Data collected in the along-track interferometry (ATI)
mode can be used to measure ocean current velocities.† Two pairs of antennas, one C-band and one L-band, separated along
the body of the plane, are used to collect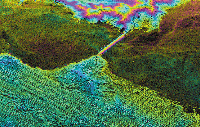 ATI data. ATI data.
Measuring
Current Movement Along-track interferometry radar data collected in the area of the
Golden Gate Bridge, San Francisco, California.
Colors in the water indicate differences in the direction and
amount of current movement as water flows into and out of the bay.
|
|
|
|
AIRSAR Technology Research
AIRSAR enables
researchers to develop and test new radar technologies for spaceborne
operations. Polarimetric SAR instrumentation demonstrated by AIRSAR was
flown as the shuttle imaging radar-C (SIR-C) mission in 1994.
More recently, the February 2000
Shuttle Radar Topography Mission mapped the world with a technique
similar to, and demonstrated by, AIRSARís TOPSAR mode. An 80MHz
bandwidth option - achieving 1.5m resolution - has been incorporated into
AIRSAR in support of a future spaceborne radar mission.
Currently under
development are modes which combine polarimetry with cross-track
interferometry and along-track interferometry.
AIRSAR Data Applications
AIRSARís
polarimetric and interferometric capabilities provide data for a wide
range of applications including biomass estimation, soil moisture
measurements, vegetation classification, land-use classification, slope
estimates for natural hazard studies, along-track interferometry to
measure coastal currents, wetland and
flooded forest classification, natural hazard monitoring, geologic
mapping, and glacier studies.
AIRSAR Data Collection
AIRSAR data are
collected for NASA-funded investigators as well as for other
organizations. Once the area and dates for the flight season are scheduled
and approved by NASA Headquarters, JPL plans data collection at selected
investigatorís sites and works with the investigators to optimize their
collection. Data are
processed at JPL and delivered
to the investigators for analysis.
All processed data are archived at JPL and catalogued on-line (http://airsar.jpl.nasa.gov.)
|
|
|
|
|
Table: AIRSAR Data
Specifications
|
Parameters
|
20 MHz
P-L-C POLSAR
and TOPSAR
|
40 MHz
P-L-C POLSAR
and TOPSAR*
|
80 MHz
L-band
POLSAR only
|
|
Data Swath
Width (range)
|
15 km
|
10 km
|
5 km
|
|
Slant Range
Resolution
|
6.7 m
|
3.3 m
|
1.6 m
|
|
DEM Posting
|
10 x 10 m
|
5 x 5 m
|
NA
|
|
Pixel spacing(x,y)
|
10x10 m
|
5x5 m
|
3x3 m
|
|
RMS Height
Accuracy (z)
C-band :
1-5 meters
1-5 meters
NA
L-band
2-10 meters
2-10
meters
NA
|
|
Image
Calibration (magnitude)
Absolute:
3 dB
3dB
3dB
Relative: 0.2
dB cross polarization, 1.5 dB between frequencies
|
* FCC prohibits
collection of P-band 40MHz within the United States
|
|
|



